Temperature-dependent transport measurements with Arduino
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.4279/pip.100007Keywords:
Microcontroller, Arduino, Transport, EducationAbstract
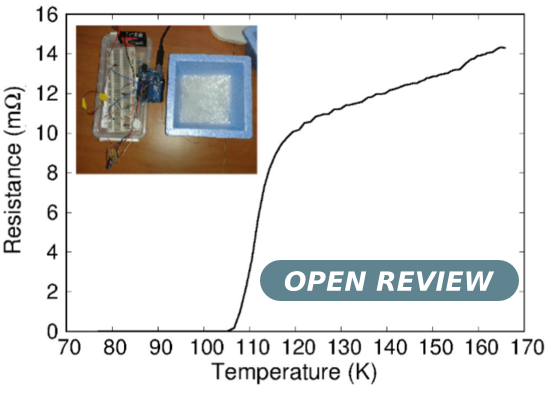
The current performances of single-board microcontrollers render them attractive, not only for basic applications, but also for more elaborate projects, amongst which are physics teaching or research. In this article, we show how temperature-dependent transport measurements can be performed by using an Arduino board, from cryogenic temperatures up to room temperature or above. We focus on two of the main issues for this type of experiments: the determination of the sample temperature and the measurement of its resistance. We also detail two student-led experiments: evidencing the magnetocaloric effect in Gadolinium and measuring the resistive transition of a high critical temperature superconductor.
Received: 7 July 2018, Accepted: 27 September 2018; Edited by: A. Marti, M. Monteiro; Reviewed by: R. Marotti, Instituto de Física, Facultad de Ingeniería - Universidad de la República, Uruguay; DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.4279/PIP.100007
Cite as: A Hilberer, G Laurent, A Lorin, A Partier, J Bobroff, F Bouquet, C Even, J M Fischbach, C A Marrache Kikuchi, M Monteverde, B Pilette, Q Quay, Papers in Physics 10, 100007(2018)
This paper, by A Hilberer, G Laurent, A Lorin, A Partier, J Bobroff, F Bouquet, C Even, J M Fischbach, C A Marrache Kikuchi, M Monteverde, B Pilette, Q Quay, is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors agree to the PIP Copyleft Notice













