Granular discharge rate for submerged hoppers
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.4279/pip.060009Keywords:
Granular physics, Bottlenecks, CloggingAbstract
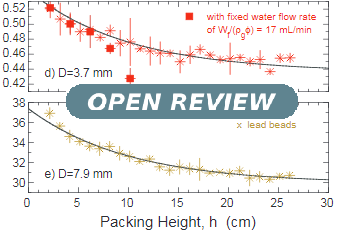
The discharge of spherical grains from a hole in the bottom of a right circular cylinder is measured with the entire system underwater. We find that the discharge rate depends on filling height, in contrast to the well-known case of dry non-cohesive grains. It is further surprising that the rate increases up to about twenty five percent, as the hopper empties and the granular pressure head decreases. For deep filling, where the discharge rate is constant, we measure the behavior as a function of both grain and hole diameters. The discharge rate scale is set by the product of hole area and the terminal falling speed of isolated grains. But there is a small-hole cutoff of about two and half grain diameters, which is larger than the analogous cutoff in the Beverloo equation for dry grains.
Received: 11 September 2014, Accepted: 10 October 2014; Reviewed by: L. Staron, CNRS, Universite Pierre et Marie Curie, Institut Le Rond d'Alembert, Paris, France; Edited by: L. A. Pugnaloni; DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.4279/PIP.060009
Cite as: T J Wilson, C R Pfeifer, N Meysingier, D J Durian, Papers in Physics 6, 060009 (2014)
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2014 T. J. Wilson, C. R. Pfeifer, N. Mesyngier, D. J. Durian

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors agree to the PIP Copyleft Notice













